I used to think sheet metal was just for cars and rooftops.
That’s all I ever saw it used for. Until one day, a client asked me to help make a small, shiny box for a medical device. It had to be strong, clean, and built just right. I had no idea sheet metal could do all that.
I started digging into things I’d never heard of—cleanroom rules, tight fitting parts, and special metals that don’t rust. It opened my eyes.
If you’re wondering where else sheet metal is used, you’re not the only one. I’ve been there too—learning bit by bit through real projects.
In this article, I’ll show you 7 different industries that count on sheet metal every day. You’ll see real examples, and I’ll explain why it matters.
By the end, you’ll know where sheet metal is used, how it’s used, and how this can help you with your own work or ideas.
Let’s dive in together!
1. Automotive and Transportation
The first time I toured a vehicle plant, I was shocked by how much of the car was just thin sheets of metal.
Everything from the hood to the trunk. Even the battery trays were made from it.
If you’re working in this space—or thinking about it—sheet metal isn’t just an option. It’s the norm.
Why Use Sheet Metal
There are 3 big reasons:
- It’s Strong but Lightweight: That matters for fuel efficiency and safety.
- It’s Affordable at High Volumes: Once you make the tools, you can press out thousands of parts quickly.
- It Supports Complex Shapes and Safety Features: Engineers can design curves, crumple zones, and even hidden welds that protect passengers during a crash.
In short, it saves money, cuts weight, and supports safety.
Common Uses
- Vehicle Body Panels: like doors, roofs, and bumpers
- Mounting Brackets: to hold parts like headlights and sensors
- Battery Trays: often for electric vehicles
- Rail and Bus Parts: including door frames, siding, and paneling
Production Needs
- Tight Tolerances: Parts must fit perfectly or the line stops.
- Anti-rust Coatings: Cars face water, salt, and mud. Coated metal holds up longer.
- Robot Compatibility: Parts need to work with robotic welding, stamping, and assembly.
Key Points
Parts made with sheet metal are lightweight, strong, and perfect for mass production with precision.
However, they must meet strict quality standards, resist rust, and work with robotic systems—or they may slow down the assembly line.
2. Electronics and Consumer Devices
Back when I helped assemble my first desktop PC, I didn’t think twice about the metal case holding everything together.
But later, while working on product sourcing for small consumer electronics, I realized just how important those thin metal enclosures really were. They weren’t just shells—they protected circuits, controlled heat, and shaped the entire look of the product.
If you’re designing or sourcing electronics, sheet metal is probably playing a bigger role than you think.
Why Use Sheet Metal
In electronics, space is tight. Parts have to be small, cool, and safe.
That’s where sheet metal works well:
- Good Heat Control: Metals like aluminum spread heat, helping parts last longer.
- Strong, but Thin: You can build light cases that still hold their shape and protect delicate internals.
- Shielding: Metal blocks electrical interference, which keeps signals clean and devices working right.
It’s not just about protection—it’s part of how the device performs. At MachMaster, we offer thin-gauge sheet metal parts with smooth finishes, tight tolerances, and reliable thermal performance—ideal for electronics and consumer device applications.
Common Uses
- Laptop and Desktop Housings: Strong, slim frames that hold ports, screens, and fans
- Smartphone Parts: Internal brackets and antenna shields
- Television and Monitor Enclosures: For both support and heat flow
- Appliances and Power Tools: Panels, brackets, and control boxes
Production Needs
- Tight Dimensions: Parts need to line up with ports, buttons, and screens
- Smooth Edges and Coatings: To avoid scratches, shocks, or short circuits
- Custom Design Support: Many parts need bending, laser cutting, or CNC punching to get the right fit and look.
Key Points
Sheet metal offers clean finishes, supports heat flow, and fits tight spaces in modern devices.
However, poor batch consistency or sharp edges can cause fit issues, overheating, or signal problems.

3. Medical Equipment and Devices
I remember visiting a hospital warehouse years ago. I was there to check on packaging, but something else caught my attention—the metal frames on every piece of equipment.
From hospital beds to portable carts, most of them had one thing in common: sheet metal.
If you’re working with medical devices, there’s a good chance sheet metal is part of the picture—even if it’s hidden behind a coat of paint or plastic cover.
Why Use Sheet Metal
In healthcare, everything needs to be clean, safe, and built to last. Sheet metal fits that need.
Here’s why it works well:
- Hygienic and Durable: Stainless steel resists rust, stains, and bacteria.
- Flexible Design: Sheet metal can be bent and shaped into trays, cabinets, and device covers.
- Fast Production: Once tooling is done, parts can be made quickly and reliably.
At MachMaster, we offer medical-grade sheet metal components with smooth surfaces, corrosion resistance, and exact fit—made to meet the high demands of medical environments.
Common Uses
- Monitor Carts and Mobile Workstations: Metal frames keep them sturdy during movement
- Diagnostic Machines: Covers and structural parts for MRI, CT, or ultrasound equipment
- Sterilization Trays and Cabinets: Easy to clean and resistant to corrosion
- Bed Frames and IV Poles: Built to hold weight and withstand daily use
Production Needs
- Smooth Surfaces: Sharp edges can harm patients or staff
- Corrosion Resistance: Hospitals use strong cleaners every day
- Tight Tolerances: Parts must align perfectly with electronic components or medical sensors
Key Points
Sheet metal is durable, easy to sterilize, and works well in clean medical environments.
However, even small defects or rough edges can risk patient safety or fail hygiene standards.
4. Industrial Machinery and Automation
The first time I walked through a factory floor, I was blown away by how many moving parts there were. Conveyor belts, safety enclosures, motor housings—they were all built with one material in common: sheet metal.
If you’re building machines or setting up automated systems, sheet metal plays a key role in keeping everything running smoothly, safely, and efficiently.
Why Use Sheet Metal
Factories are rough environments. Parts need to hold up under heat, vibration, and daily wear. Sheet metal makes that possible.
Here’s why it works so well:
- Strong Under Stress: It can support motors, gears, and tools without bending or cracking.
- Easy to Shape: Sheet metal can be bent, cut, and welded into frames, guards, or brackets.
- Protective: It creates covers and barriers that keep dust, oil, and debris away from moving parts.
It’s not just about strength—it’s also about safety and speed.
Common Uses
- Machine Frames and Cabinets: For CNC machines, presses, and robotic arms
- Guarding Panels and Covers: To keep workers safe and machines clean
- Control Boxes and Sensor Mounts: Holding wiring, switches, and buttons
- Material Handling Systems: Parts like chutes, trays, and brackets for conveyors
Production Needs
- Dimensional Accuracy: So parts fit tightly with minimal gaps
- Durable Finishes: To resist oil, heat, and wear over time
- Weldable and Machinable: So fabricators can add holes, slots, or mounts without cracking
Key Points
It holds up under stress, resists heat, and supports custom shapes for moving equipment.
However, without tight dimensions or strong coatings, parts may wear down or fail during operation.

5. Aerospace and Defense
When I held a small aircraft bracket in my hand for the first time, I was shocked by how light it felt. It was solid, shaped perfectly—and made from sheet metal. That moment stuck with me. In this industry, every gram counts.
If you’re working with aircraft, drones, satellites, or defense systems, sheet metal isn’t just useful. It’s critical.
Why Use Sheet Metal
Aerospace and defense demand the highest level of performance. Materials need to be light, strong, and stable under pressure.
Sheet metal fits that need in a few key ways:
- Lightweight Strength: Aluminum and titanium sheets offer a high strength-to-weight ratio.
- Precision Shaping: Sheet metal can be cut and bent to exact dimensions for complex parts.
- Thermal Resistance: Metals like titanium and stainless steel handle high heat without warping.
In the air or on the battlefield, there’s no room for failure.
Common Uses
- Airplane Skins and Panels: Covering the wings and fuselage
- Avionics Brackets and Trays: Holding electronics inside cockpits and satellites
- Missile Components: Lightweight bodies and fin structures
- Military Equipment Cases: Durable transport boxes for gear and tools
Production Needs
- Tight Tolerances: Even a small shift can affect how a part fits or performs in flight
- Certified Materials: Only certain metals are approved for use in aerospace
- Traceability: Every part must be tracked from raw material to finished product
Key Points
Metal parts are lightweight, heat-resistant, and shaped with extreme precision for flight or defense.
However, one wrong spec or missing traceability record can lead to part rejection or safety failure.

6. Construction and Architecture
On a recent site visit, I watched a team install wall panels and stair railings at surprising speed.
What made it possible? Sheet metal.
It was used across the build—roof panels, HVAC ducts, framing brackets, even decorative details on the facade. It reminded me how much this material does in both form and function.
If you’re involved in construction or architecture, sheet metal may already be part of your workflow. If not, it’s worth a closer look.
Why Use Sheet Metal
Construction demands materials that last, work well under pressure, and look good too. Sheet metal checks those boxes.
Here’s why it’s so useful:
- Weather Resistance: Materials like galvanized steel and aluminum don’t break down in harsh outdoor conditions.
- Easy to Work With: Sheets can be cut, formed, and shaped off-site or on-site.
- Flexible for Design: Architects use it for both structure and visual appeal.
It’s durable and versatile—great for both the inside and outside of buildings.
Common Uses
- Roofing and Siding: Tough skins that protect the building
- HVAC Systems: Air ducts for heating and cooling
- Architectural Features: Wall panels, canopies, and cladding
- Support Structures: Staircases, handrails, and framing connectors
Production Needs
- Consistent Sizing: So you don’t waste time recutting on-site
- Surface Protection: Paint or coatings to prevent corrosion
- Custom Options: Like perforations, bends, or laser-cut patterns
Key Points
Sheet metal adds durability, weather protection, and clean design to modern builds.
However, delays in delivery or inaccurate sizing can impact deadlines and drive up costs.

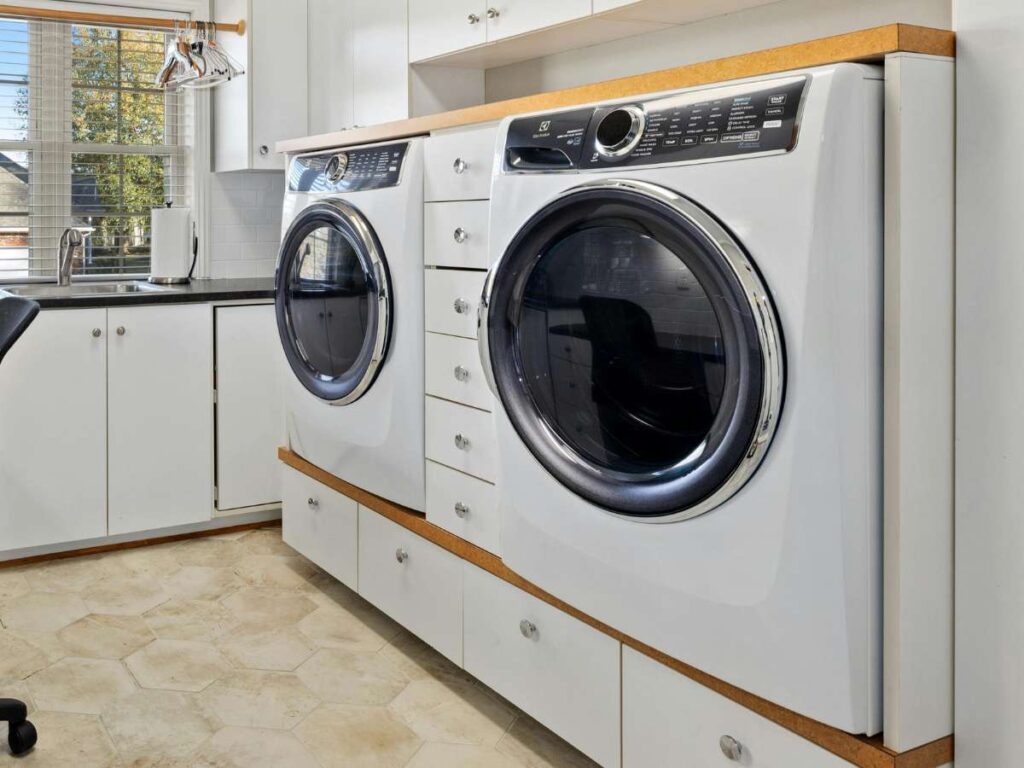
7. Furniture and Home Appliances
During a move, it’s easy to miss the materials behind the things you use every day. But take a closer look—bed frames, oven doors, drawer slides—they often have one thing in common: sheet metal.
It’s inside the fridge, under the washing machine, and in the legs of your office chair.
If you’re involved in furniture or appliances, this material likely plays a bigger role than you realize.
Why Use Sheet Metal
Furniture and appliances need to be tough. They also need to look clean and work smoothly every day.
Here’s why sheet metal fits so well:
- Strength and Support: It can hold weight without bending. Great for frames, legs, and brackets.
- Smooth Surface Finish: Powder coating and paint stick well, so the final product looks sharp.
- Easy Forming: Metal sheets can be stamped or bent into parts that match modern designs.
It’s a balance of form and function—and sheet metal helps deliver both.
Common Uses
- Appliance Exteriors: Like washers, dryers, and refrigerators
- Internal Supports: Inside ovens, stoves, and control panels
- Furniture Frames and Legs: Metal adds strength without bulk
- Drawers and Hinges: Thin, strong pieces that slide and pivot with precision
Production Needs
- Clean Edges and Coatings: No sharp corners or flaking paint
- Precise Fit: Doors, panels, and drawers must align just right
- Batch Consistency: Every piece must match, especially mass-market furniture
Key Points
It brings strength, clean looks, and long-lasting performance to daily-use products.
However, even slight misalignment or poor coating can make a product feel cheap or wear out too fast.

Conclusion
You’ve now seen how 7 very different industries all use sheet metal—each in their own way.
From aerospace to furniture, it’s shaping the products people rely on every single day.
It’s not just about material. It’s about precision. Strength. Reliability.
The right decision now can save you time, cost, and future stress.
Need help getting started? Contact us today.
Discover More Options
There’s so much more to discover! Check out our other products and find what fits your needs:
- Anodizing Service
- CNC Milling Service
- CNC Turning Service
- Injection Molding Service
- CNC Machining Service
For more helpful content, explore our collection of recommended reads:
Still haven’t found what you’re looking for? Don’t hesitate to contact us. We’re available around the clock to assist you.







