I’ve tried manual machining. Casting. Injection molding.
Each one worked—for a while. Until parts came back warped or delivery ran late.
Eventually, I realized the problem wasn’t the process.
It was the fit.
You might be in the same spot now trying to match your production needs with the right process. CNC machining looks promising, but you don’t want to overspend or overengineer.
That’s why I wrote this guide.
To give you a real look at how CNC machining fits into different industries. What it solves. Where it shines. And where it might not be the best move.
This article will help you make that call. It’s not a pitch. It’s a tool—so you can decide what works best for your parts, your customers, and your bottom line.
So let’s start!
1. Aerospace & Defense
The first time I worked on a part of aerospace, I remembered the pressure. One mistake could mean a failed test. Or worse, something is going wrong in the air.
That’s why this industry doesn’t cut corners.
Aircraft and defense systems rely on CNC machining for a simple reason: precision. Tolerances in aerospace are often measured in microns. That’s smaller than a human hair. And the materials? Tough stuff. Think titanium and Inconel—both are hard to machine but needed because they handle extreme heat and stress.
These aren’t just any parts:
- Turbine blades
- Engine housings
- Electronic enclosures
- Structural brackets
Each one has to survive vibration, heat, and pressure. There’s no room for error.
That’s where CNC shines.
What Buyers Should Know
If you’re thinking about using CNC for aerospace or defense, you’ll need more than a good machine. You’ll need a shop that meets strict quality standards.
Two certifications matter most:
- AS9100: A quality system developed specifically for aerospace
- ISO 9001: A general quality management standard, often required in this space
Shops in this industry often use:
- 5-axis CNC machines
- Multi-axis lathes
- In-process inspection tools
- Final part validation with coordinate measuring machines (CMMs)
Sound like overkill? Maybe. But in this industry, it’s just how things work.
Common Problems Solved
Before CNC, many aerospace parts were hand-fitted or cast. That took time and often led to rework. CNC solved a few key problems:
- Speeds up prototyping during R&D
- Cuts down error in safety-critical parts
- Replaces slow, manual fabrication processes
Have you ever wondered if CNC is too much for your project? Or not enough?
Aerospace proves one thing: If your parts need to hold up under pressure—literally—CNC might be the safest way forward.
2. Automotive
Back when I helped a small parts supplier transition to CNC, I didn’t expect such a huge shift. We went from hand-fabricated brackets to CNC-machined parts that actually fit the first time. Fewer returns. Fewer delays.
And happier clients.
In the automotive world, CNC machining plays a big role behind the scenes. You’ll find it in:
- Engine blocks
- Gearbox components
- Custom brackets and mounts
- Dashboards and interior panels
- Electrical housings
It’s also a go-to tool during early design and testing. Before a car hits the road, teams need test parts—fast. CNC helps build those test parts without the delay of tooling up for mass production.
Need a custom-fit bracket for a prototype? CNC can make it overnight.
Now that you’ve seen where CNC shows up, let’s talk about what buyers should watch for.
What Procurement Teams Should Consider
Not all CNC shops are the same. If you work in automotive sourcing, you need consistency. That means:
- High repeatability: making the same part, again and again, without variation
- Knowledge of materials: from aluminum to cast iron to specialty plastics
Many shops combine CNC with other processes like:
- Die casting: shaping metal using a reusable mold
- Injection molding: for high-volume plastic parts
This combo keeps things efficient—prototypes from CNC, then switch to casting or molding once the design is finalized.
Still wondering what CNC adds to the mix?
Let’s look at the practical side.
CNC Helps With
- Speeding up the tooling process
- Shortening development cycles
- Meeting strict automotive standards like ISO/TS 16949, which focuses on quality management in the automotive supply chain
If you need parts that are reliable, repeatable, and production-ready, CNC might be the piece that brings your build together.
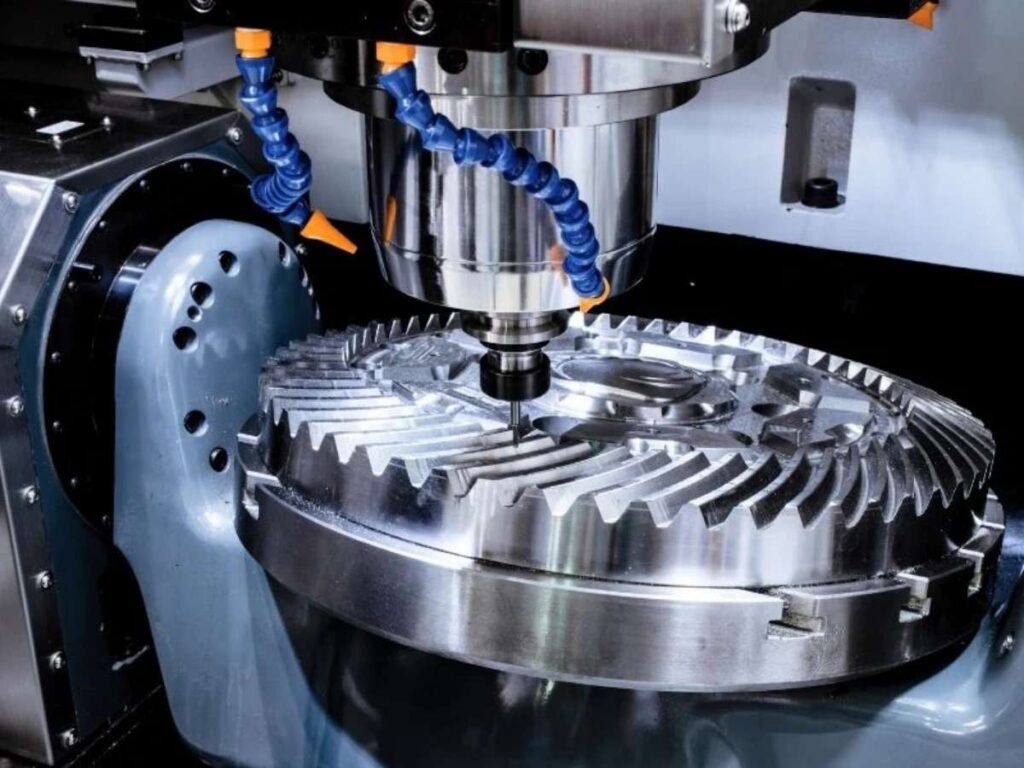

3. Medical Devices
I still remember holding a machined implant part in my hand for the first time. It was small, simple, and smooth. But knowing it would go inside someone’s body? That changed how I looked at precision forever.
CNC machining is a quiet but vital part of healthcare manufacturing. It helps make:
- Surgical tools
- Implants like bone plates and screws
- Prosthetics
- Diagnostic housings
- Custom enclosures for sensitive equipment
When you’re dealing with people’s health, accuracy isn’t optional. Every surface, edge, and angle matters.
But materials matter just as much.
Key Requirements
Medical parts often use specific materials. You’ll hear names like:
- Titanium: strong, lightweight, and biocompatible
- PEEK: a plastic that resists chemicals and heat
- Stainless steel: easy to sterilize
- Medical-grade plastics: used in devices and housings
But choosing the right material is only the start. The way parts are made matters too. Many components must be machined in cleanroom environments to avoid contamination.
And the standards? They’re strict. Most projects need to follow:
- FDA guidelines for medical device safety
- ISO 13485: a standard for quality management in medical manufacturing
Now that you know the requirements, let’s talk about what designers should keep in mind.
Tips for Product Designers
If you’re designing a medical product, you don’t have time for guesswork. Here’s what helps:
- Work with a CNC partner that offers material traceability: the ability to track where every material came from
- Prototype early: test how the part feels and works before paying for production tooling
- Don’t rush revisions—small design changes can save lives down the line
Are you building a device meant to help someone heal, recover, or move again?
If yes, CNC gives you precision and the repeatability you need to make that possible.
If you’re looking for a partner with experience in medical-grade CNC parts, MachMaster is ready. We’re ISO 9001 certified and deliver parts with ±0.01 mm tolerance—trusted by teams in the medical and diagnostics field.
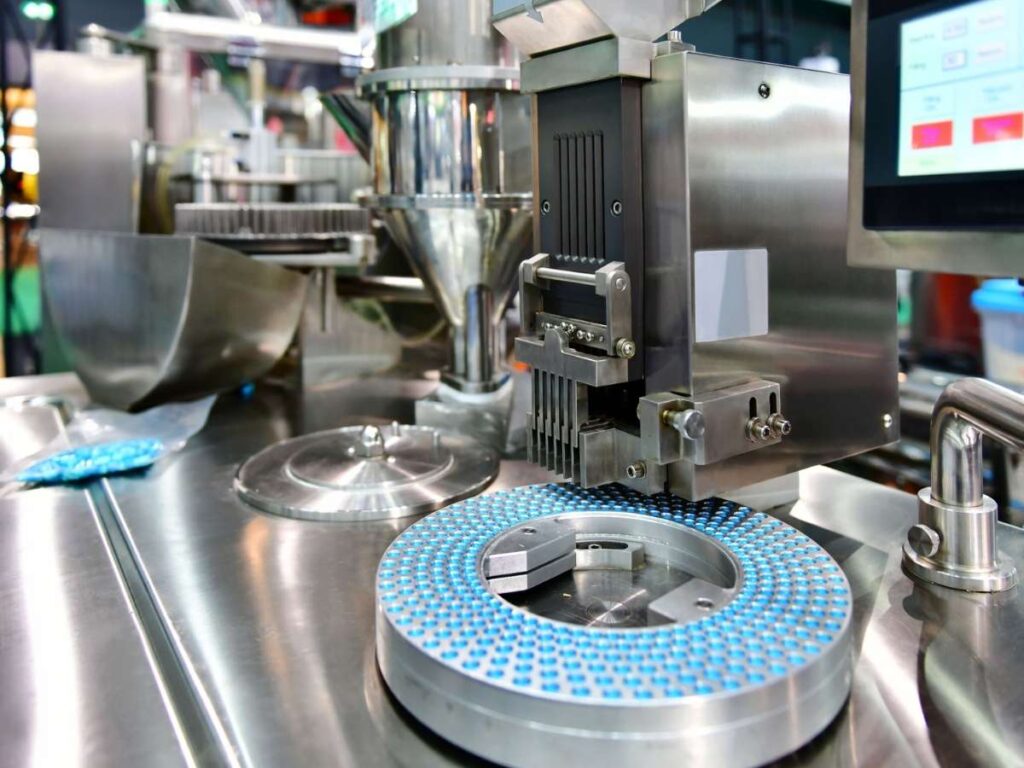

4. Electronics & Robotics
I once helped a friend build a prototype for a small home robot. The electronics were solid. The code worked. But the parts didn’t fit together.
Turns out, 3D printing wasn’t strong enough—and the tolerances weren’t tight.
So we switched to CNC.
That change made everything click. Literally.
In electronics and robotics, CNC machining shows up in places you might not expect. Think:
- Enclosures for circuit boards
- Housings for sensors
- Custom aluminum heat sinks
- Brackets and jigs for testing
- Fixtures that hold small assemblies
- Gears and mounts for robotic arms
These parts don’t just need to look clean—they need to function under real stress, heat, or movement.
Now let’s talk about why engineers and builders love CNC during development.
For R&D Engineers and Makers
CNC makes life easier when you’re experimenting.
If you’re working in research and development, or even building a small robotic arm in your garage, you probably need parts fast. And you probably need to tweak them more than once.
CNC machining lets you:
- Iterate on designs quickly
- Test fit and function before committing to a mold
- Create low-volume runs for specialty setups or one-off builds
That flexibility matters when you’re still figuring things out.
Now, how do you find the right CNC supplier for these kinds of jobs?
Sourcing Insights
Look for vendors who offer:
- Quick turnaround times
- Surface finishing like anodizing or powder coating
- Experience working with aluminum and engineering plastics
Ask them how they handle design changes. Or how they communicate during the quoting process. Do they feel like a partner or just a part maker?
If you’re building something smart, mobile, or connected, CNC might be what brings your parts into the real world—fast, accurate, and ready to test.
5. Consumer Products
A while back, I worked with a startup that was building a small kitchen gadget.
The design was sleek. The idea had promise. But no one wanted to commit to a big production run before seeing how it felt in someone’s hand.
That’s where CNC came in.
For consumer products, CNC machining is a solid tool for development. It’s especially helpful for:
- Device cases
- Handles and knobs
- Display unit frames
- Buttons and dials
- Parts for wearable devices
When you’re still shaping your idea—literally—CNC gives you the freedom to try things out without waiting weeks for tooling.
Now, let’s talk about what this means if you’re running a business or managing a product launch.
Benefits to Business Owners
You don’t always need thousands of parts. Sometimes, you just need ten. Or one.
That’s where CNC helps:
- Makes it easier to test your minimum viable product (MVP)
- Allows for pilot runs without long lead times
- No minimum order quantities (MOQs), which means less risk
- Let’s gather feedback early and adjust quickly
Wondering how to make that first version of your product without wasting money?
CNC might be your answer.
Of course, there are a few things to think through first.
What to Watch Out For
Material choice really matters here. It affects:
- How the part looks
- How it holds up to wear
- How heavy or light the product feels
CNC machining is great for rigid parts—like metal or hard plastics. But if your design needs something soft or bendable, you may want to look into silicone casting or urethane molding instead.
If you’re building a physical product and need something real in your hands, CNC gives you that next step—without locking you into full-scale production too early.
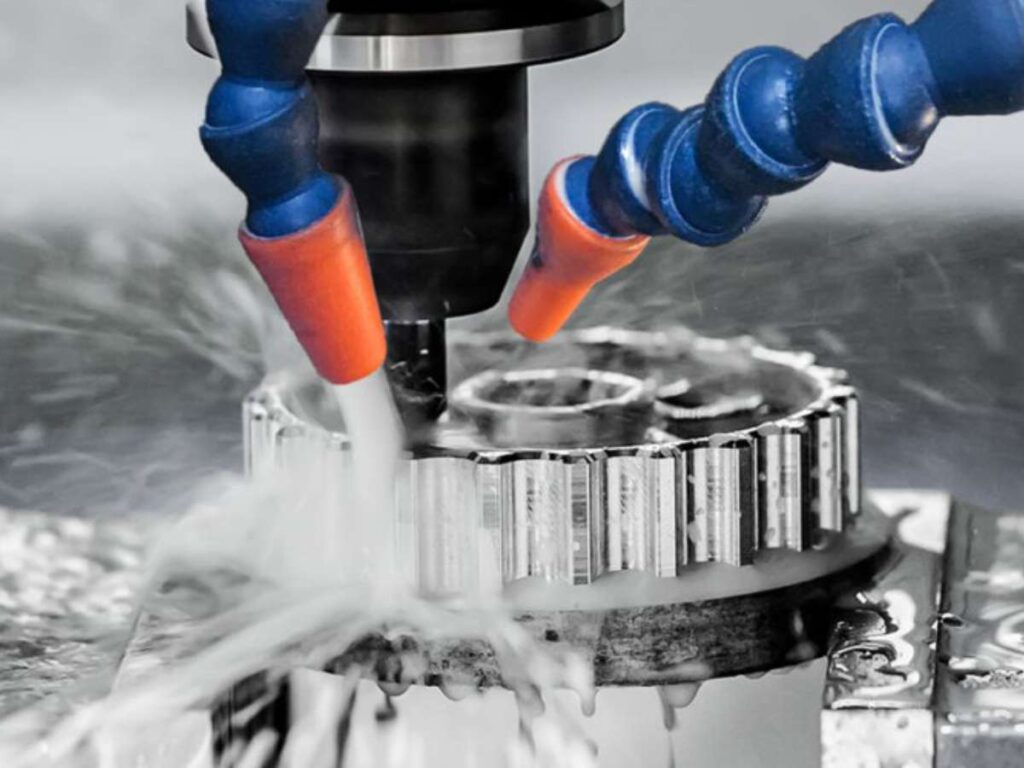

6. Industrial Equipment & Machinery
A few years ago, a factory manager called me in a panic. One of their older machines failed. The part they needed didn’t exist anymore—no backups, no supplier, no drawings.
We reverse-engineered it and machined a new one in two days. That single part saved them from weeks of downtime.
In industrial settings, that kind of thing happens more often than you’d think.
CNC machining is used for:
- Shafts
- Gears
- Bearings
- Housings
- Support brackets
- Structural frames
It also comes in handy when you need custom spare parts for legacy machines or discontinued models. No long wait. No hunting through catalogs.
For custom parts that need to fit legacy machines or new builds with no room for error partners, like MachMaster provide full CNC support, from quick prototyping to production-ready runs.
Ideal For
If you’re managing machines or running a production line, this section is for you.
CNC works well for:
- Factory and shop floor owners
- Equipment maintenance teams
- B2B machinery suppliers who deal with custom builds
Whether you’re dealing with broken parts or building new systems, CNC adds flexibility without slowing you down.
So how exactly does it help in day-to-day operations?
CNC Solves
- Reduces downtime by producing custom replacements fast
- Supports build-to-order models where every piece is slightly different
- Fits into just-in-time supply chains—where parts arrive exactly when needed, not before
Have you ever waited weeks for a critical part to ship?
Or had to modify something just to make it work?
CNC lets you take control of those moments. You get exactly what you need, when you need it—and often with better accuracy than the original.
7. Furniture & Interior Design
A few years ago, I helped a friend build a small line of modern chairs. The designs were beautiful but every leg had to be cut at the exact same angle or the chair wobbled.
Hand-cutting didn’t cut it. So we moved to CNC.
In furniture and interior design, CNC machines bring accuracy and consistency. You can use them for:
- Chairs and tables
- Lighting fixtures
- Wall panels and ceiling tiles
- Custom shelving
- Decorative pieces and accents
When you’re working with patterns, curves, or tight joints, getting those details right every time really matters.
Now let’s look at who benefits most from this setup.
Perfect for
CNC machining is especially useful for:
- Interior designers who need repeated parts with exact measurements
- Furniture makers working on small batch runs
- Artists and builders who mix form and function
Need matching grooves on 100 panels? Want every joint to align without sanding or tweaking?
CNC gives you consistency when hand tools struggle to match.
But that consistency only pays off if the finishing is done right.
Buyer Notes
Furniture buyers and builders should know:
- CNC routers are used for wood, plastic, and soft materials
- CNC mills are better for metals like brass or aluminum
- Ask your vendor about edge finishing, sanding, and surface prep
- Make sure they offer coating or painting if your parts need color
Ever had a piece that looked great in CAD but felt rough or uneven in person?
That’s where finishing makes or breaks your final product.
If you care about clean lines, smooth edges, and repeatable designs, CNC might be what takes your vision from sketch to showroom.
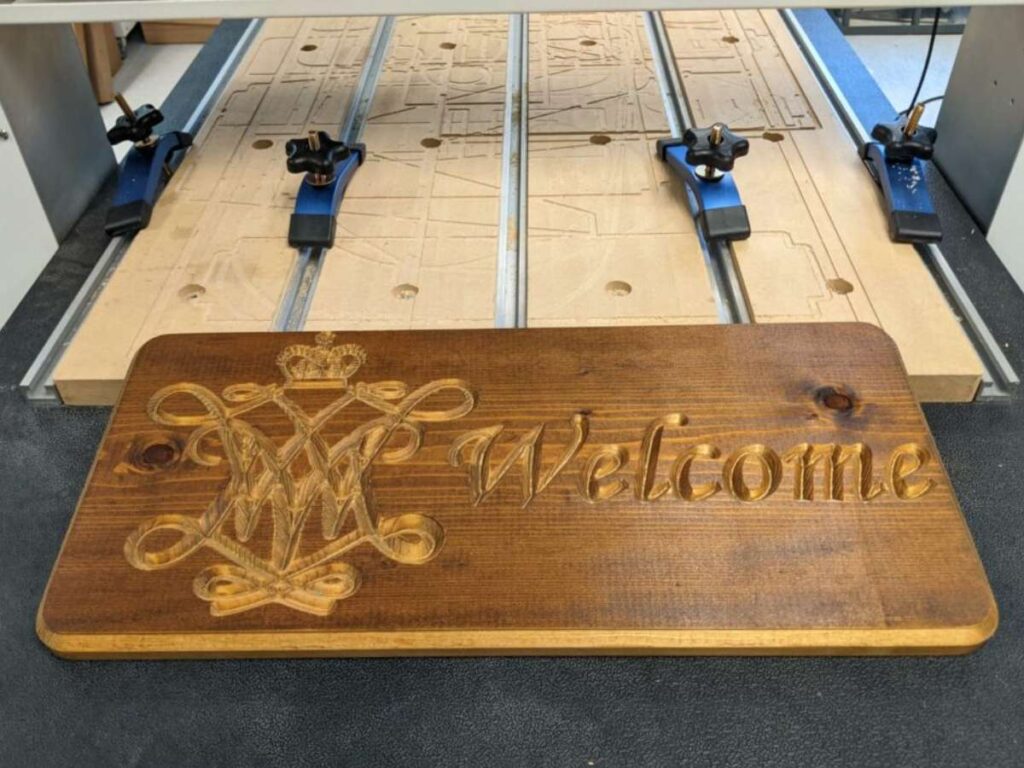

8. Education, Hobby & DIY Projects
I started with 3D printing. It was fun until my parts snapped under pressure. A guitar pedal case cracked. A drone frame warped in the sun.
That’s when I tried CNC.
And everything was held together.
For hobbyists, students, and DIY builders, CNC machining opens up a whole new level of strength and accuracy. It’s popular for:
- RC model parts
- Musical instruments
- Cosplay props and costume pieces
- School or college engineering prototypes
- Custom tools or accessories
CNC doesn’t just make parts—it makes parts that last. If you’re tired of reprinting the same piece over and over, this might be your next step.
So how do you get started without feeling overwhelmed?
Advice for Beginners
CNC can feel technical at first. But you don’t have to dive in all at once.
Here’s where to begin:
- Start with beginner-friendly brands like Sainsmart or Inventables
- Learn the steps:
- CAD (Computer-Aided Design): design your part
- CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing): create the toolpath
- G-code: the instructions your machine follows
- Machine setup: load material, set origin, press go
Most machines come with support groups and tutorials. Take your time. Mess up. Learn by doing.
You might be surprised at how fast it clicks.
CNC also fits well in classrooms and maker spaces. It teaches problem-solving, patience, and how to turn an idea into something real.
Ever held a part that came out exactly the way you imagined it?
That’s the moment CNC becomes more than just a tool—it becomes part of your creative process.

Conclusion
We’ve covered aerospace. Medical. Furniture. Robotics.
But what really matters is your product. Your challenge. Your idea.
CNC machining can help—if the fit is right.
Now you’ve seen where it works. How it works. Why does it work.
You’ve seen how I’ve used it. And how others do too.
So what’s holding you back?
Start small. Start simple. Just start.
If you’re wondering whether CNC can help your product get off the ground…
Let’s chat. Contact us today.
Explore More Helpful Resources
There’s more to explore! Check out our additional product selections to find exactly what you’re looking for:
Still haven’t found what you’re looking for? Don’t hesitate to contact us. We’re available around the clock to assist you.







